The Crucial Role of IC Qualification for RFID Transponders in Automotive and Industrial Applications
In the rapidly advancing world of technology, Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) transponders have become ubiquitous in various sectors, notably in automotive and industrial applications. These tiny, yet powerful devices play pivotal roles in tracking, security, and automation. Central to their functionality is the integrated circuit (IC) embedded within, whose performance and reliability dictate the efficiency of the RFID transponder. Given the critical importance of these applications, IC qualification, especially under standards like AEC-Q100 for automotive uses, becomes indispensable. This article explores the significance of IC qualification for RFID transponders, underlining its vital role in ensuring the transponders’ reliability, safety, and performance in demanding automotive and industrial settings.
Understanding IC Qualification
IC qualification is a comprehensive testing and certification process that assesses whether semiconductor products meet specific industry standards for quality, performance, and reliability. For RFID transponders, which are extensively used in both automotive and industrial environments, the ICs must endure extreme conditions without faltering. The qualification process involves subjecting these ICs to a series of rigorous tests designed to simulate the harsh environments they will encounter in real-world applications.
Automotive Applications and AEC-Q100
In the automotive sector, RFID transponders are utilized for a myriad of applications including keyless entry systems (e.g., immobilizer), tire pressure monitoring, and part tracking throughout the supply chain. The environment within automotive applications can be incredibly harsh, with wide temperature ranges, constant vibration, and exposure to moisture and chemicals.

Fig 1: RFID transponder use in automotive applications.
To address these challenges, ICs for automotive RFID transponders must be qualified to the AEC-Q100 standard, which is specifically designed for automotive-grade electronic components. This standard outlines a set of stress tests, including temperature cycling, power and temperature stress, and device lifespan testing. AEC-Q100 qualification ensures that the ICs can withstand the automotive environment’s rigors, thereby guaranteeing the reliability and functionality of the RFID transponders throughout the vehicle’s lifetime.
Industrial Applications: Beyond the Basics
Industrial applications of RFID transponders span across inventory management, asset tracking, process control, and access control, among others. Like their automotive counterparts, RFID transponders in industrial settings must operate reliably under challenging conditions. However, industrial environments can vary significantly, exposing RFID transponders to extreme temperatures, dust, moisture, shock, and vibrations.
IC qualification for industrial RFID transponders, therefore, goes beyond basic standards to encompass a wider range of stress tests. These tests are designed to ensure that the ICs can endure the specific conditions of their intended industrial environments. Industrial IC qualification involves an extensive analysis of the IC’s performance over time, under continuous stress, and in varied environmental conditions, ensuring their long-term reliability and effectiveness.

Fig 2: RFID transponder use in industrial applications – wafer fabrication process.
Key Importance of IC Qualification
Reliability and Performance
The cornerstone of IC qualification for RFID transponders in both automotive and industrial applications is to ensure unparalleled reliability and performance. In environments where failure or malfunction can lead to significant consequences, including compromised safety, operational downtime, and financial losses, the importance of reliability cannot be overstated. Through rigorous qualification processes, manufacturers can guarantee that the RFID transponders will perform as expected, under all conditions, throughout their intended lifespan.
Safety
In automotive applications, the safety implications of RFID transponder failure can be severe. For instance, a malfunctioning RFID-based tire pressure monitoring system could fail to alert the driver of under-inflated tires, potentially leading to accidents. Similarly, in industrial settings, an unreliable RFID transponder could result in the loss of critical equipment or failure to maintain hazardous materials securely. IC qualification ensures that such risks are mitigated by confirming that the RFID transponders can reliably perform their safety-related functions.
Compliance and Market Access
Adhering to established standards like AEC-Q100 for automotive applications or specific industrial qualification criteria helps manufacturers comply with regulatory requirements. This compliance is not just about meeting legal obligations; it also assures customers of the product’s quality and reliability, facilitating easier market access and acceptance. In highly regulated sectors, such as automotive and industrial markets, this can be a significant competitive advantage.
Cost-Efficiency
Investing in the IC qualification process might seem costly at first glance, but it is fundamentally a cost-saving measure in the long run. By ensuring that the RFID transponders are reliable and durable, manufacturers can avoid the costs associated with recalls, warranty claims, and reputational damage. Additionally, the use of qualified ICs in RFID transponders can reduce maintenance and replacement costs, offering a better return on investment over the product’s lifecycle.
Different Criteria for Automotive and Industrial Qualification
While both automotive and industrial applications require IC qualification for RFID transponders, the specific criteria and tests can vary, reflecting the unique challenges of each environment.
Automotive Qualification (AEC-Q100)
- Temperature Range: automotive ICs must operate over a wider temperature range, typically from -40°C to +150°C, to account for engine heat and cold environments. The temperature ranges may vary depending on the environment use, which the automotive grade classifications are as follows: Grade 0 spans from -40°C to +150°C, Grade 1 covers -40°C to +125°C, Grade 2 is from -40°C to +105°C, and Grade 3 operates within -40°C to +85°C. These ranges are set to ensure that components can withstand the various operating environments they may be exposed to within automotive applications. The higher the grade, the more extreme the temperature the component can endure, which is particularly crucial for parts located in under-the-hood applications where temperatures can be remarkably high.
- Vibration and Shock: tests simulate the constant vibration and shocks experienced during driving to ensure mechanical robustness.
- Moisture Resistance: given the exposure to humidity and potential water ingress in automotive environments, moisture resistance is critical.
Industrial Qualification
- Chemical Resistance: industrial RFID transponders might be exposed to various chemicals, necessitating ICs that can withstand such environments.
- Extended Lifespan: many industrial applications require a longer lifespan for RFID transponders, demanding ICs that can maintain performance over time, even beyond the typical automotive requirements.
- Custom Environmental Conditions: depending on the specific industrial setting, additional tests may be necessary to simulate unique conditions like extreme dust, continuous operation, or exposure to corrosives.
Ensuring Excellence: Silicon Craft’s Commitment to Rigorous
IC Qualification Standards for RFID Transponders
At Silicon Craft, the integrity of our development process is exemplified by our steadfast adherence to the stringent protocols of IC qualification, ensuring that our SIC61 series for automotive use (include aftermarket) and SIC73 series for industrial use stand up to the exacting standards of today’s dynamic markets. Our commitment to rigorous testing and compliance with key standards such as AEC-Q100 and JEDEC is a testament to our dedication to delivering products that excel in reliability, safety, and performance.
As RFID technology evolves, the importance of robust IC qualification continues to be paramount, forming the backbone of successful and reliable system integration in both automotive and industrial spheres.
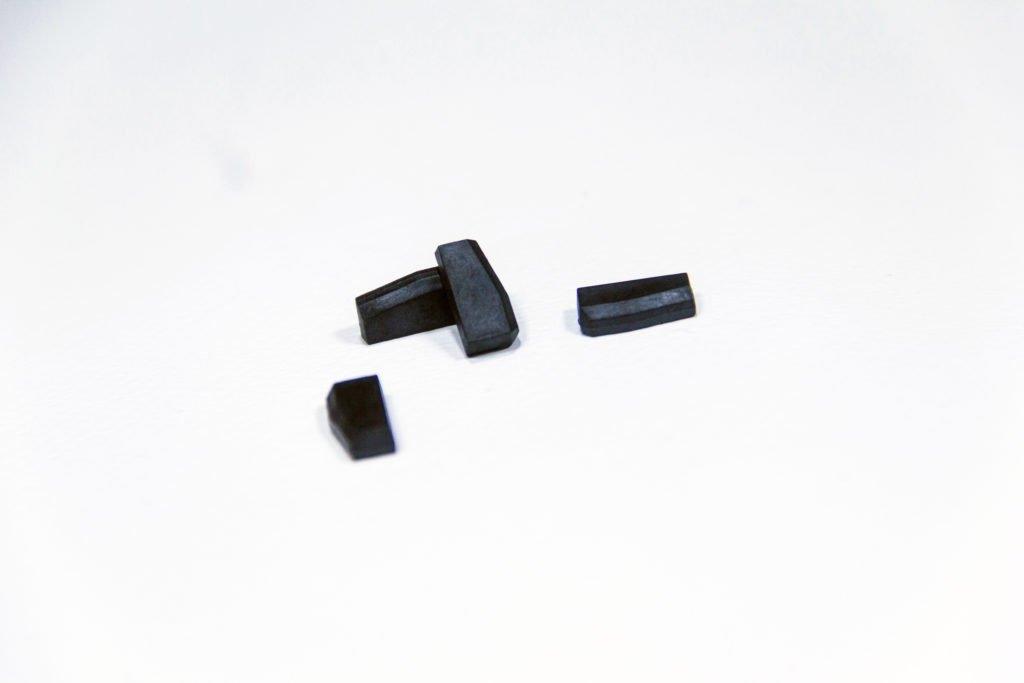

Fig 3: Silicon Craft’s automotive transponder series,
including SIC6149, SIC618A, and SIC6147, are AEC-Q100 qualified for reliable operations.
With Silicon Craft, customers and partners are empowered with confidence, knowing they are adopting solutions at the pinnacle of quality and safety, driving innovation, and leading the charge in industry advancements.